Research Highlights
Scientists Discover Key Information About the Function of Mitochondria in Cancer Cells
PET-guided multi-modality imaging to characterize spatial architecture of mitochondrial networks in non-small-cell lung cancer
15-03-2023 UCLA Health
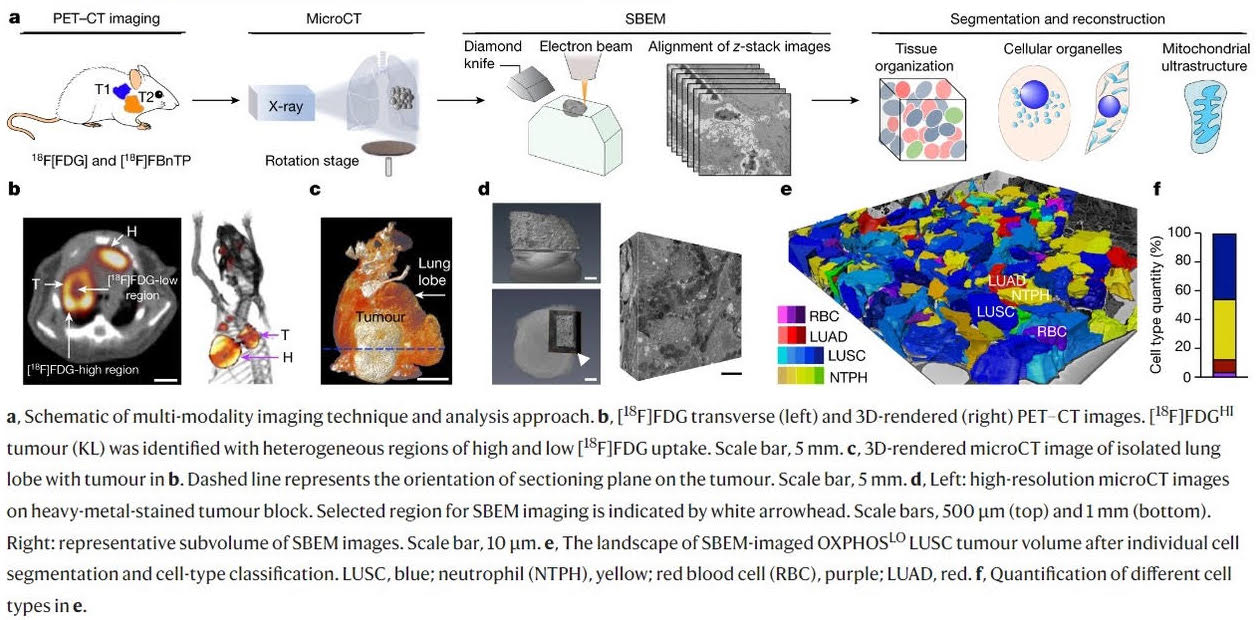
In a new study, published in Nature, researchers from the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center, in collaboration with the National Center for Microscopy and Imaging Research (NCMIR) at UC San Diego, used positron emission tomography (PET) in combination with electron microscopy to generate 3-dimensional ultra-resolution maps of mitochondrial networks in lung tumors of genetically engineered mice. They categorized the tumors based on mitochondrial activity and other factors using an artificial intelligence technique called deep learning, quantifying the mitochondrial architecture across hundreds of cells and thousands of mitochondria throughout the tumor.
The authors examined two main subtypes of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) -- adenocarcinomas and squamous-cell carcinomas and found distinct subpopulations of mitochondrial networks within these tumors. Importantly, they discovered that the mitochondria frequently organize themselves with organelles such as lipid droplets to create unique subcellular structures that support tumor cell metabolism and mitochondrial activity.
The study was led by Mingqi Han, Ph.D., a post-doctoral researcher in the lab of David Shackelford, Ph.D. Dr. Shackelford is a UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center member and Associate Professor of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine at the UCLA David Geffen School of Medicine.
The authors anticipate that mitochondrial populations in human cancer samples will not be mutually exclusive to their respective tumor subtype, but rather there will be a spectrum of activity.
The investigators say these findings provide key information about the function of mitochondria in cancer cells and could lead to new approaches to cancer treatment.
"Our study represents a first step towards generating highly detailed 3-dimensional maps of lung tumors using genetically engineered mouse models," said Dr. Shackelford. "Using these maps, we have begun to create a structural and functional atlas of lung tumors, which has provided us valuable insight into how tumor cells structurally organize their cellular architecture in response to the high metabolic demands of tumor growth. Our findings hold promise to inform and improve current treatment strategies while illuminating new directions from which to target lung cancer."
"Our study has uncovered a novel finding in the metabolic flux of lung tumors, revealing that their nutrient preference may be determined by the compartmentalization of their mitochondria with other organelles, either relying on glucose ("sugar") or free fatty acids ("fat")," said Dr. Han. "This discovery has important implications for developing effective anti-cancer therapies that target tumor-specific nutrient preferences. Our multi-modality imaging approach has enabled us to uncover this previously unknown aspect of cancer metabolism, and we believe that it can be applied to other types of cancer, paving the way for further research in this area."
In an associated article summary (briefing), the editorial team at Nature expounded on the significance of the multi-modality imaging approach, “This work by Han et al. stood out to us because of the impressive range of experimental methodologies. The authors were able to study heterogeneity of mitochondrial structures and function in vivo, in models of distinct lung cancer subtypes. These findings were complemented by 3D ultrastructural microscopy, to which the authors also applied a deep-learning neural-network approach.” Professor Mark Ellisman, Director of NCMIR foresees this integrated approach will immediately benefit studies in other organ systems including pancreas, retina, and other brain regions where mitochondrial function is high (and whose alteration is impactful to disease).
Nature Briefing:
https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-00427-0
Original Article:
Mingqi Han, Eric A. Bushong, Mayuko Segawa, Alexandre Tiard, Alex Wong, Morgan R. Brady, Milica Momcilovic, Dane M. Wolf, Ralph Zhang, Anton Petcherski, Matthew Madany, Shili Xu, Jason T. Lee, Masha V. Poyurovsky, Kellen Olszewski, Travis Holloway, Adrian Gomez, Maie St. John, Steven M. Dubinett, Carla M. Koehler, Orian S. Shirihai, Linsey Stiles, Aaron Lisberg, Stefano Soatto, Saman Sadeghi, Mark H. Ellisman, David B. Shackelford. Spatial mapping of mitochondrial networks and bioenergetics in lung cancer. Nature, 2023; DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-05793-3